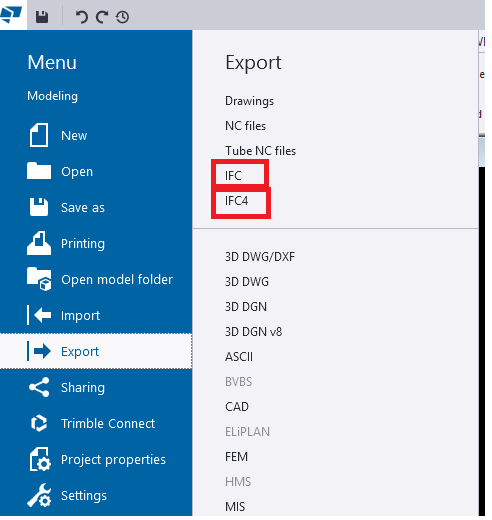
When we export models from TEKLA Structures, we mainly see two options:
- Export IFC (this mostly means IFC2x3 format)
- IFC4 Export
Both formats serve the same purpose—model interoperability—but they work differently, support different levels of data, and offer different quality of geometry.
In this blog, we explore the key differences, benefits, and when to use each format.
1. What is “Export IFC” (IFC2x3)?
This is the old IFC format used by most companies for many years.
Key points
- Works in almost all BIM software
- Shows Geometry is basic and sometimes rough
- Limited property information
- The File size is Bigger
Best For
✔ General coordination
✔ Clients who request IFC2x3
✔ Old software compatibility
2. What is “IFC4 Export”?
This is the newer and more advanced format.
Key Points
- Geometry looks cleaner and smoother
- Curved members (Hollow sections, pipes, elbows, etc.) look perfect
- More detailed data (bolts, welds, assemblies)
- Smaller file size in many cases
- Better for new BIM tools
Best For
✔ Modern BIM tools
✔ Better visual quality
✔ Detailed model sharing
3. Quick Comparison
| Feature | IFC2x3 (Export IFC) | IFC4 |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Basic (Rough) | Smooth & Accurate |
| Curved Shapes | Approximate | Perfect & Precise |
| File Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Compatibility | Very High | Medium |
| Details | Limited | More Detailed |
| convert IFC object to Steel Member | Work well | Can’t convert |
4. Which One Should You Use?
- Use Export IFC (IFC2x3) if the client asks for it or if compatibility is important.
- Use IFC4 if you want cleaner geometry and more detailed information.
5. Final Summary
- IFC2x3 (Export IFC) → Best for compatibility
- IFC4 → Best for quality and smooth geometry
If your client or BIM Execution Plan (BEP) does not specify the format, use IFC4 for best geometry
Leave a Reply